Independence Day of Sri Lanka, 4 February
 Sri Lanka has had a continuous record of human settlement for more than two millennia, and its civilization has been shaped largely by that of the Indian subcontinent. The island’s two major ethnic groups, the Sinhalese and the Tamils, and its two dominant religions, Buddhism and Hinduism, made their way to the island from India, and Indian influence pervaded such diverse fields as art, architecture, literature, music, medicine, and astronomy.
Sri Lanka has had a continuous record of human settlement for more than two millennia, and its civilization has been shaped largely by that of the Indian subcontinent. The island’s two major ethnic groups, the Sinhalese and the Tamils, and its two dominant religions, Buddhism and Hinduism, made their way to the island from India, and Indian influence pervaded such diverse fields as art, architecture, literature, music, medicine, and astronomy.
Despite its obvious affinities with India, Sri Lanka nevertheless developed a unique identity over the ages that ultimately set it apart from its neighbour. Cultural traits brought from India necessarily underwent independent growth and change in Sri Lanka, owing in part to the island’s physical separation from the subcontinent. Buddhism, for instance, virtually disappeared from India, but it continued to flourish in Sri Lanka, particularly among the Sinhalese. Moreover, the Sinhalese language, which grew out of Indo-Aryan dialects from the mainland, eventually became indigenous solely to Sri Lanka and developed its own literary tradition.
Source:
History of Sri Lanka. (n.d.). https://www.britannica.com/place/Sri-Lanka/History
Relationship between Sri Lanka and Assumption University of Thailand
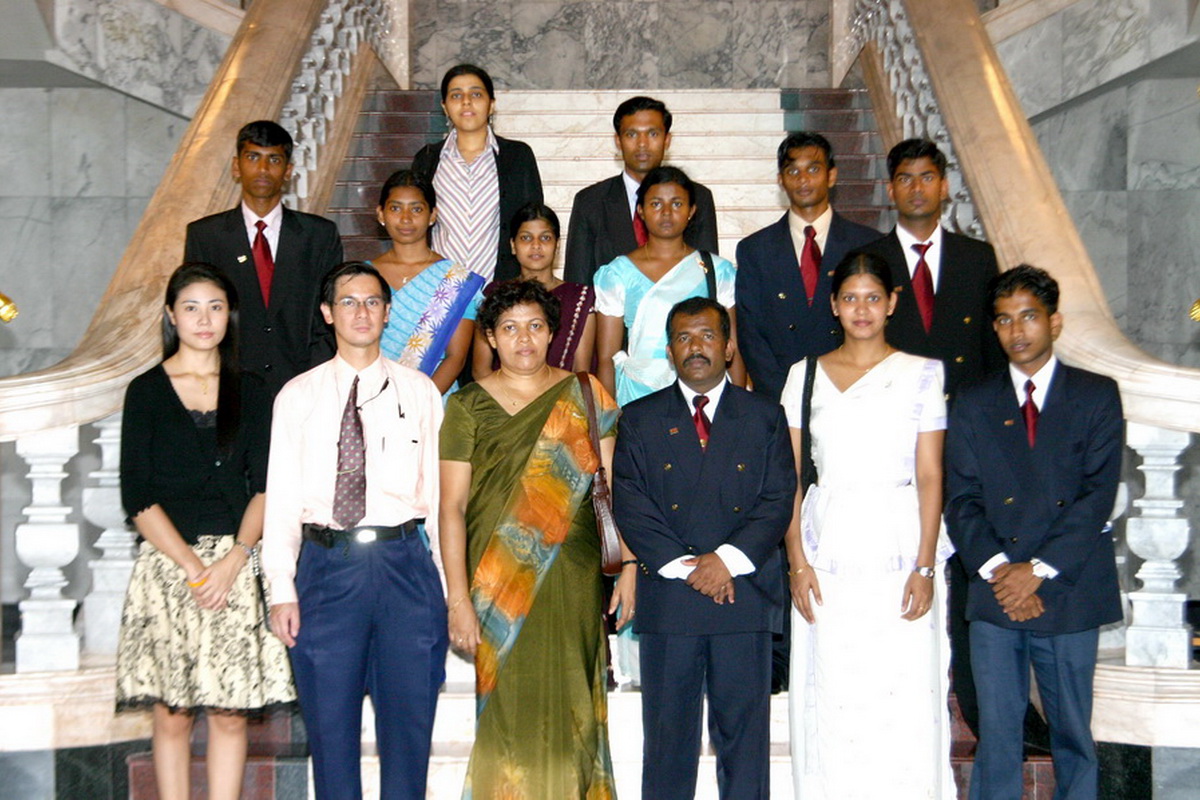
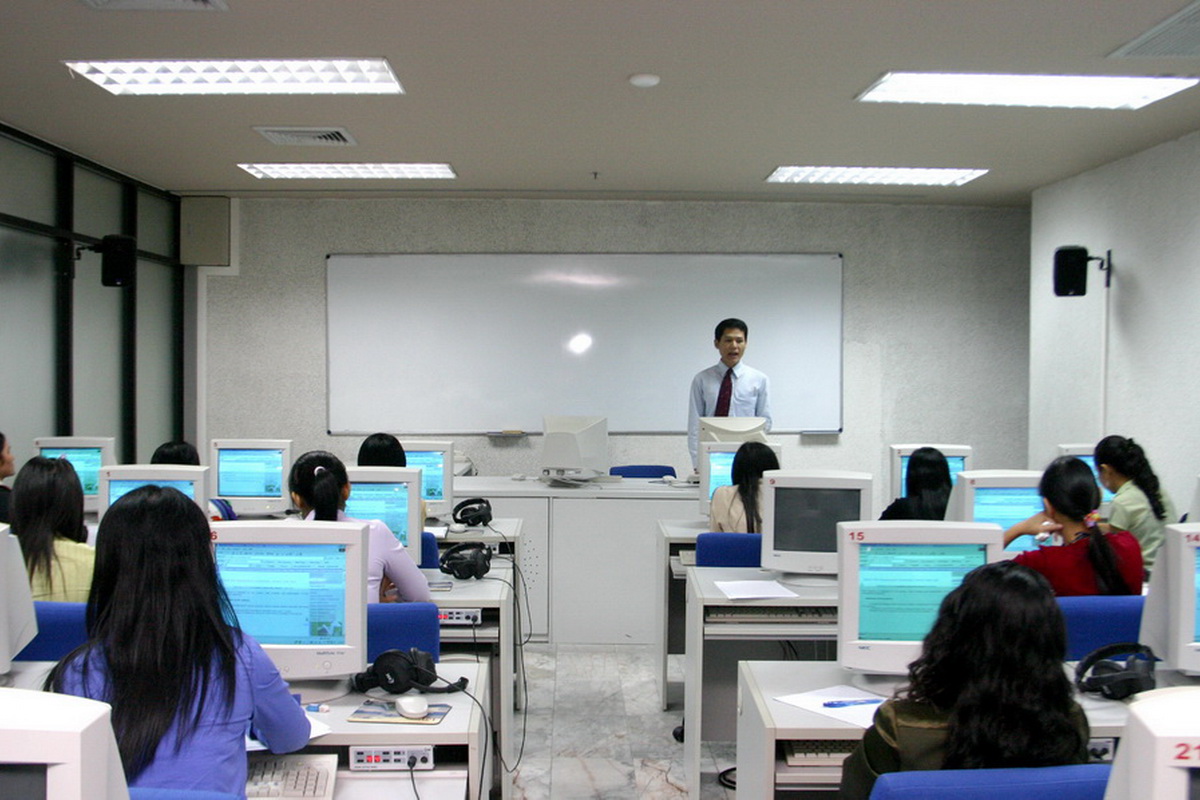


Upcoming Events

Happy! Independence Day of Estonia
